



Next: Experiment: The Full Wave
Up: DC Power Supplies
Previous: Half-Wave Single-Sided Supply
We observed that in the half-wave rectifier, we lost half of our signal.
To take advantage of the entire signal we construct a
power supply with the full-wave rectifier
which is shown in Fig. 1.5.
Figure 1.5:
Full-Wave Supply with Step-Down Transformer
 |
To transform this signal into an almost constant DC value,
we filter it using the same procedure as for the half wave rectifier
and power supply. Only this time the ripple voltage should be approximately
half of what it was before, since the capacitor will discharge for
half the time as it did for the half-wave case. Thus, the AC ripple
will be given by
| 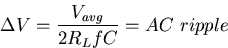 |
(8) |
Neil Goldsman
10/23/1998
